» Surge Power Conditioning
» Need Electrical Help? Ask the Electrician
Communications Frequency Glossary
|
By Dave Rongey
Summary: This glossary will serve as a guide o the various terms associated with the use of frequencies and the devices that are dependant upon them. © By: Dave Rongey |
Electrical Systems and Communication Devices
Frequencies Glossary
Advances in electricity, electronics and new technology require the use of frequencies to enable the associated devices to function and perform a specific task.
Because of this frequencies are all around us.
This glossary will serve as a guide o the various terms associated with the use of frequencies and the devices that are dependant upon them.
Antenna: A wire or set of wires used to send and receive radio waves.
Cell Phone: A wireless telephone that sends and receives messages using radio frequency energy in the 800-900 megahertz portion of the radio frequency (RF) spectrum.
Cell Tower: A tower style antenna system that is part of a communications network used to send and receive signals to cell phones.
Cell Site: Another name for a cellular base station.
Cellular Base Station: Antennas and electronic equipment used to receive and transmit cellular telephone signals.
Cordless Telephone: A portable telephone that transmits signals over a small distance to a receiver that is wired into the telephone network. Cordless telephones are generally used only in or around one’s home.
Electromagnetic Energy: Waves of electrical and magnetic energy moving together through space. Also called electromagnetic radiation.
Electromagnetic Field: An area containing electromagnetic energy (electromagnetic radiation).
Electromagnetic Radiation: Waves of electrical and magnetic energy moving together through space. Also called electromagnetic energy.
ERP (Effective Radiated Power) - A measure of how well an antenna concentrates the radiated energy in a specific direction. An analogy can be drawn in a comparison between an ordinary light bulb and a spotlight. At a given distance, the light that falls on a surface in the beam of a 100 W spotlight is much brighter than that from an ordinary 100 W bulb at the same distance, because the spotlight concentrates the light into a beam. Correspondingly, the light that falls on a surface that is not in the beam of the spotlight is much less than that from the ordinary light bulb at the same distance.
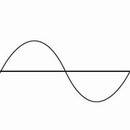
Frequency: The number of waves passing a given point in one second. Measured in Hertz (Hz), or cycles per second.
Hertz: The unit of measurement used to describe the frequency of a wave. One Hertz (Hz) is equal to one cycle of the wave per second.
Microwave (MW) - An electromagnetic wave with a wavelength between about one millimeter and 30 centimeters corresponding to a frequency between 300 GHz and 1 GHz.
Microwaves: A subset of radio waves that have frequencies ranging from around 300 million waves per second (300 MHz) to three billion waves per second (3 GHz).
Radio Frequency (RF) - frequencies of electromagnetic waves between approximately 3 kHz (3,000 Hz) and 300 GHz (3 x 1011 Hz). Sometimes, a distinction is drawn between radio waves, which have frequencies between 3 kHz and 1 GHz, and microwaves, which have a frequency between 1 GHz and 300 GHz.
Radio Waves: Electromagnetic energy with frequencies in the 3000 hertz (3 kHz) to 300 billion Hertz (300 GHz) portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio frequency Energy: Another name for radio waves.
RF Energy: An abbreviation for Radio Frequency Energy.
Smart Meter: Smart Meters, (also called AMI, or AMR) are part of the "Smart Grid", which is part of a wireless system installed on our homes, businesses, and in most communities around the world. The smart meter system is typically installed without consent and without full disclosure of how they work. Some areas are banning the installtion of smart meters over various concerns including EMF polution and health related concerns.
Telecommunications: The transmission of words, sounds, or images, usually over great distances, in the form of electromagnetic energy, for example by telegraph, telephone, radio, or television.
Wireless Telephone: A hand-held phone with a built-in antenna that transmits signals through the air without a physical connection. Cell (cellular), PCS, mobile, car, and bag (transportable) phones are all considered wireless telephones. Cordless telephones used only in or around one’s home are not considered wireless telephones.
RESOURCES:
The EMF Safety Network
The EMF Safety Network is a sponsored project of the Ecological Options Network (EON). The EMF Safety Network continues to pursue justice on smart meters and EMF pollution.
Listen to what EMF Noise Sounds Like
Hear the sounds of EMF noise.
The Safest Way to Test Electrical Devices and Identify Electric Wires!The Non-Contact Electrical TesterThis is a testing tool that I have had in my personal electrical tool pouch for years, and is the first test tool I grab to help identify electrical wiring. It is a Non-contact tester that I use to easily Detect Voltage in Cables, Cords, Circuit Breakers, Lighting Fixtures, Switches, Outlets and Wires. Simply insert the end of the tester into an outlet, lamp socket, or hold the end of the tester against the wire you wish to test. Very handy and easy to use.
The Quickest Way to Check for Faulty Electrical Wiring!The Plug-In Outlet TesterThis is the first tool I grab to troubleshoot a problem with outlet circuit wiring. This popular tester is also used by most inspectors to test for power and check the polarity of circuit wiring. It detects probable improper wiring conditions in standard 110-125 VAC outlets Provides 6 probable wiring conditions that are quick and easy to read for ultimate efficiency Lights indicate if wiring is correct and indicator light chart is included Tests standard 3-wire outlets UL Listed Light indicates if wiring is incorrect Very handy and easy to use.
Strip Off Wire Insulation without Nicking and Damaging the Electric Wire!The Wire Stripper and Wire CutterMy absolute favorite wire stripping tool that I have had in my personal electrical tool pouch for years, and this is the tool I use to safely strip electrical wires. This handy tool has multiple uses: The wire gauges are shown on the side of the tool so you know which slot to use for stripping insulation. The end of the tool can be used to grip and bend wire which is handy for attaching wire onto the screw terminals of switches and outlets.. The wire stripper will work on both solid and stranded wire. This tool is Very Handy and Easy to Use. |
||
Residential Electrical Parts and AccessoriesLight Switches 120volt Outlets Circuit Breakers Electrician Tools Voltage Testers |














